| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
| |
|
| |
This is a technique usually adopted by small, traditional farmers. Selected durian seeds from selected varieties are germinated in germinating trays. The seedlings are then transferred to polybags containing soil mixtures after 4 weeks. Suitable polybags measuring 23.0 cm x 31.5 cm are filled up with soil mixture of top soil, fertiliser and sand in 7:3:2 or 3:2:1 proportions. The seedlings are ready for field planting after 5 months. However, durian is heterogenous in nature thus the seedlings produced may not be true to type and not similar to the original parent. Seedling trees also have a longer juvenile period. |
| |
|
| |
This is a more efficient and recommended method of propagation. Durian trees are usually propagated by budding or grafting onto a rootstock . They are budded at about 5-10 cm from soil level. Budding and grafting are only different means to the same end. In both cases a piece of a variety to be grown as a new tree is taken from a tree of the required variety and is joined to a rootstock where it unites and grows. For budding a single bud is taken, while for grafting a shoot with several buds is taken. Rootstocks from 7 weeks old seedlings are suitable for grafting and 4 months old seedlings are suitable for budding .
Another, less popular method of grafting is the union technique. The union technique requires the rootstock to be brought close the shoot as illustrated in the figure below. Similar cuts are made on the scion and the rootstock . The two cut parts are fused together with a strong tape. Support is necessary to be given to the shoot seedling. After 3-4 weeks the shoots from the rootstock is removed and the shoot from the required variety is separated from the mother plants below the fusion point. The seedlings are ready for planting after 3 months.
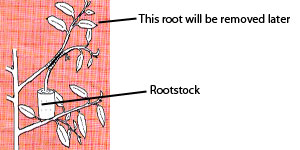
|
| |
|
| |
| This asexual method has never been practiced commercially. This method is only resorted to, in order to save the required clones for germplasm collection. The juvenile period for this method may be longer. |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| |
| |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
| Names |
| |
|
|
|
Durio zibethinus |
|
|
Common: |
|
English: |
Durian |
Indonesia: |
Durian
|
Malaysia: |
Durian |
Tagalog: |
Durian |
Thai: |
Thurian |
Vietnam: |
Sau rieng |
| Mandarin: |
Liulian |
| Tamil: |
Durian |
| Khmer: |
Thouren |
| Laotian: |
Mahk tulieng |
| Burmese: |
Duyin |
|
|
Taxonomic Position: |
| |
|
Domain: |
Eukaryota |
Kingdom: |
Viridiplantae |
Phylum: |
Spermatophyta |
| Subphylum: |
Angiospermae |
Class: |
Dicotyledonae |
Order: |
Malvales |
Family: |
Bombaceae |
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
|
| |
|

